The relationship between oral health and systemic health has been a topic of growing interest in medical research, with emerging evidence suggesting a potential link between oral health conditions and heart disease. While maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for preventing dental problems, it may also have implications for cardiovascular health. In this article, we delve into the connection between oral health and heart disease, exploring the underlying mechanisms and implications for overall well-being.
Understanding the Connection:
Inflammatory Pathways:
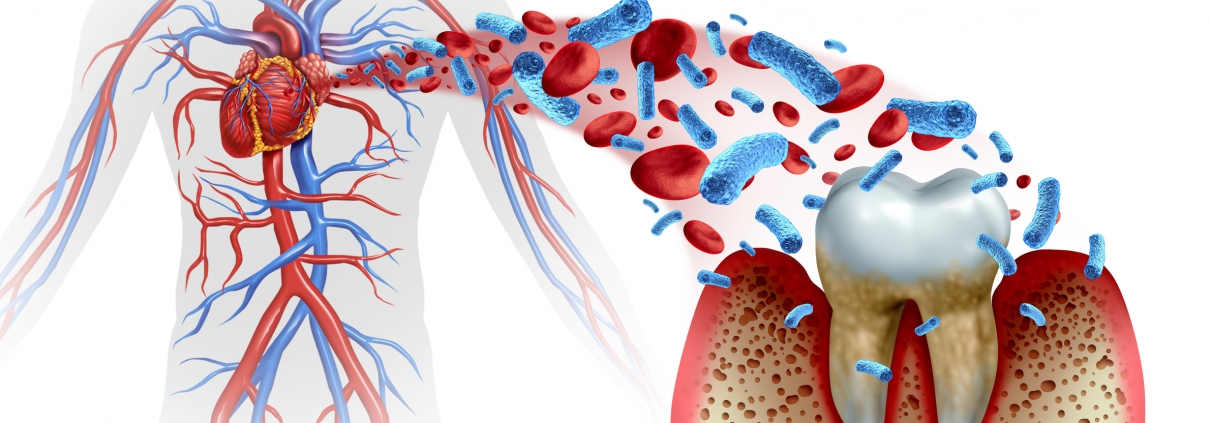
Periodontal disease, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the gums and supporting structures of the teeth, has been associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
Inflammation plays a central role in both periodontal disease and cardiovascular disease, suggesting potential shared pathways between oral and systemic inflammation.
Bacterial Translocation:
Bacteria present in the mouth, particularly those associated with periodontal disease, may enter the bloodstream through the gums and contribute to systemic inflammation.
These bacteria or their byproducts can potentially travel to other parts of the body, including the arteries, where they may exacerbate inflammation and contribute to the development of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
Shared Risk Factors:
Smoking:
Smoking is a well-established risk factor for both periodontal disease and heart disease, exacerbating inflammation and compromising overall health.
Smokers are more likely to develop periodontal disease and have an increased risk of cardiovascular events compared to non-smokers.
Diabetes:
Diabetes is another common risk factor for both oral health problems and heart disease.
Poorly controlled diabetes can impair the body’s ability to fight infections, including gum disease, and may also contribute to cardiovascular complications.
Implications for Cardiovascular Health:
Increased Risk of Heart Disease:
Studies have found associations between periodontal disease and an increased risk of heart disease, including conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke.
While the exact nature of the relationship remains under investigation, addressing oral health may have potential benefits for cardiovascular health.
Preventive Strategies:
Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups, is essential for preventing periodontal disease and potentially reducing the risk of heart disease.
Treating gum disease and addressing other oral health issues promptly may also have positive effects on cardiovascular health.
Collaborative Care:
Interdisciplinary Approach:
Collaboration between dental and medical professionals is essential for addressing the complex interplay between oral health and heart disease.
Dental visits may provide opportunities for identifying individuals at risk of heart disease and facilitating referrals for further evaluation and management.
Patient Education:
Educating patients about the connection between oral health and heart disease empowers them to prioritize preventive care and adopt healthy lifestyle behaviors.
Encouraging regular dental checkups and emphasizing the importance of oral hygiene can contribute to overall cardiovascular wellness.
The relationship between oral health and heart disease underscores the interconnected nature of the body’s systems and the importance of holistic health care. By recognizing the potential impact of oral health conditions on cardiovascular health and vice versa, individuals and healthcare providers can take proactive steps to promote overall well-being. Prioritizing good oral hygiene, addressing periodontal disease, and managing shared risk factors can contribute to a healthier mouth and heart. As research continues to unravel the complexities of this relationship, integrating oral health into comprehensive cardiovascular care may pave the way for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life. Remember, a healthy smile and a healthy heart go hand in hand—take care of both for optimal well-being.