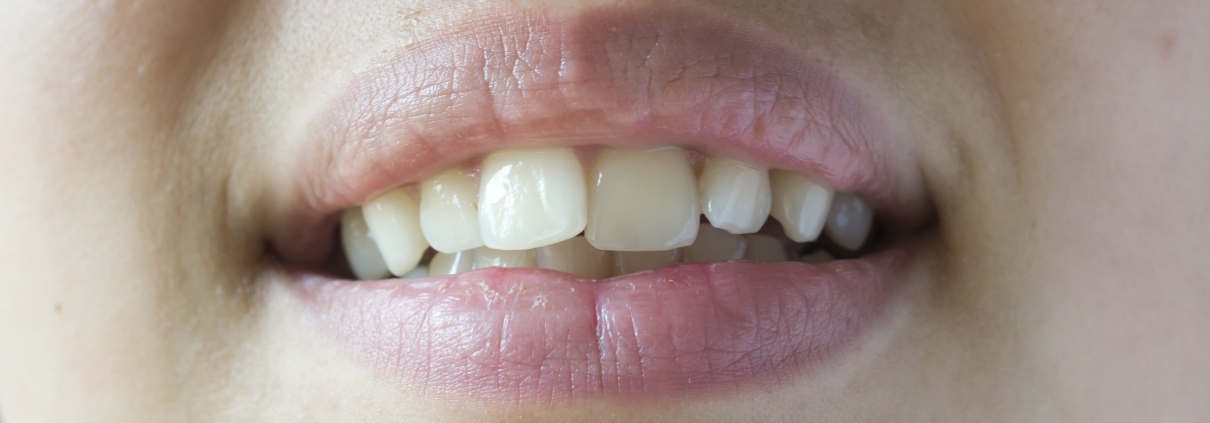
Occlusion is a term that refers to the order and regularity of teeth. Ideally, the teeth should fit snugly together and not be too tight or spaced apart. Also, none of the teeth should be crooked or crooked. The maxillary teeth should slightly cover the mandibular teeth so that the protrusions of the mandibular teeth fit into the grooves of the maxillary teeth.
Deviation from the ideal occlusion is called malocclusion. There are many types of deviations, however, deviations of any kind have many consequences. Aligning the upper teeth is essential to prevent biting the cheeks and lips, while tidying the lower teeth is essential to prevent biting the tongue.
Irregular teeth reduce self-confidence and create obstacles in social and personal life by damaging the beauty of the smile. Fortunately, orthodontics can be done in a variety of ways to align the teeth to create a more attractive smile and increase self-confidence. Orthodontic treatment covers a wide range from dental wiring to surgery to correct jaw or dental bone problems. Of course, surgery is the last resort that can be resorted to if other treatments are not effective. The irregularity of most patients’ teeth is corrected using orthodontic appliances such as braces.
Tooth disorder is usually inherited, meaning it is passed down from generation to generation. There are complications or habits such as the following that change the shape and structure of the jaw:
Cleft lip and palate (sugar lip)
Continuous sucking of the pacifier after 3 years of age
Long-term use of milk bottles in childhood
Sucking a finger in childhood
Injuries that lead to skewness and deviation of the jaw.
Tumor in the mouth or jaw
Deformed or impacted teeth
An improper restoration can cause filled, veneered, or wired teeth to not fit well together.
Obstruction of the airway (breathing through the mouth) caused by allergies or enlargement of the tonsils or the third tonsil.
The fact that the mandible is ahead of the maxilla is called the underbite. In this case, the lower teeth cover the upper teeth. This problem not only makes the face uncomfortable but also makes the patient feel pain and discomfort in the jaw when chewing and talking.
Overbite is the opposite of underbite, this time the upper jaw is ahead of the lower jaw. Overbite is sometimes so severe that the lower teeth hit the roof of the mouth, causing pain and various problems when chewing.
Crossbite is a complication in which the upper teeth are inserted into the lower teeth. Crossbite often leads to jaw deviation and complications such as temporomandibular joint disorder.
Open bite is a condition in which the upper and lower teeth do not fit well together. This problem is more common in children who suck their thumb or press their tongue against their teeth all the time.