Braces can be a game-changer for achieving a beautiful, straight smile. However, wearing braces requires extra attention to dental care to ensure optimal oral health throughout the orthodontic journey. Proper care not only keeps your teeth and braces in top condition but also reduces the risk of dental problems that could arise if oral hygiene is neglected. In this article, we will explore essential tips on how to care for your teeth when wearing braces to maintain a healthy and dazzling smile.
Brushing and Flossing
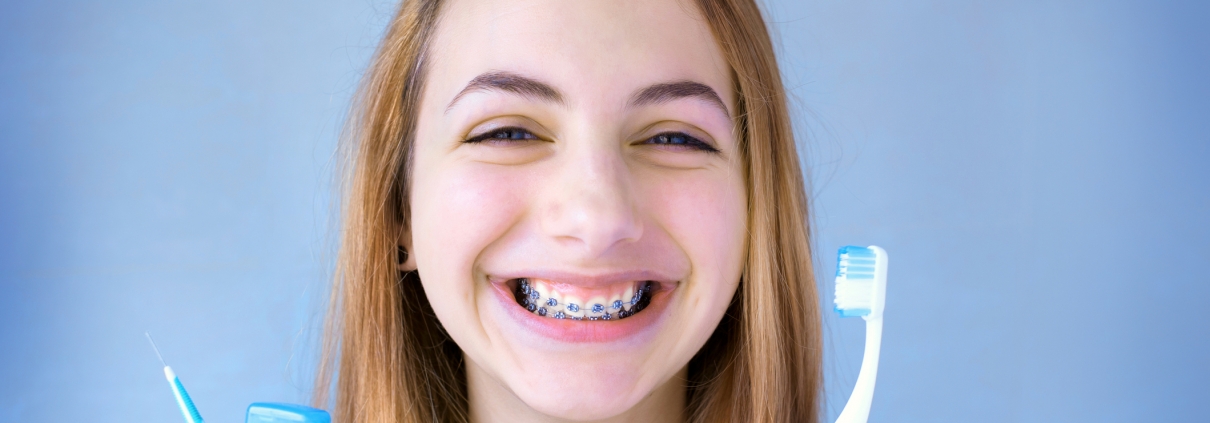
Regular brushing and flossing become even more crucial when you have braces. Aim to brush your teeth after every meal and snack to remove food particles that can get stuck between wires and brackets. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to clean each tooth thoroughly, angling the brush to reach around the brackets. Remember to clean the areas between the braces and gums gently to prevent irritation.
Flossing can be challenging with braces, but it’s vital to remove debris and plaque between teeth. Dental floss threaders or orthodontic flossers can help you navigate around wires and brackets easily. Consider using interdental brushes to clean hard-to-reach spaces, such as under the wires and around the brackets.
Rinse with Mouthwash
Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can provide an additional layer of protection for your teeth and gums. Swishing with mouthwash after brushing and flossing can help eliminate bacteria and reduce the risk of gum inflammation and other oral issues. Look for a mouthwash that is alcohol-free and recommended by your orthodontist or dentist.
Choose Your Diet Wisely
While wearing braces, it’s essential to be mindful of your diet to avoid damaging the braces and to protect your teeth from cavities. Certain foods can get stuck in the braces or bend the wires, leading to discomfort or extended treatment time. Avoid hard, sticky, or chewy foods like popcorn, gum, caramel, and hard candies. Opt for softer foods that are easier on your braces, such as mashed potatoes, yogurt, steamed vegetables, and soft fruits.
Wear a Mouthguard during Physical Activities
If you engage in sports or physical activities, wearing a mouthguard is essential to protect your teeth and braces from potential impacts or injuries. A custom-fit mouthguard made by your dentist will provide the best protection and ensure a comfortable fit over your braces.
Attend Regular Orthodontic Check-ups
Maintaining routine visits to your orthodontist is crucial throughout your braces journey. Regular check-ups will allow your orthodontist to monitor your progress, make necessary adjustments, and address any concerns or discomfort you may be experiencing. Follow your orthodontist’s advice regarding adjustments, rubber bands, and other elements of your braces to achieve the best results.
Be Mindful of Habits
Certain habits can be detrimental to your braces and teeth. Avoid biting on hard objects like pens, pencils, or ice, as this can damage the brackets and wires. Additionally, avoid nail-biting or chewing on non-food items. Habits like these can prolong treatment and lead to unnecessary repairs.
Caring for your teeth when wearing braces is not only about achieving a perfect smile, but it’s also essential for maintaining overall oral health. Following a diligent oral hygiene routine, watching your diet, and being mindful of habits will ensure your braces journey is as smooth as possible. Remember, the time and effort you invest in caring for your teeth during this period will be well worth it when you unveil your beautifully aligned smile. Always consult with your orthodontist or dentist if you have any concerns or questions about your braces care routine. Keep smiling, and your dazzling new smile will be waiting for you at the end of your orthodontic adventure.